RSA 2015 Almost every Java-hacking blackhat is now popping Adobe Flash after Microsoft's hard line patch policy made it harder to target techs such as Java.
The stricken scum now face a choice: work harder to find Java zero-day or abandon ship and start exploiting old Flash bugs.
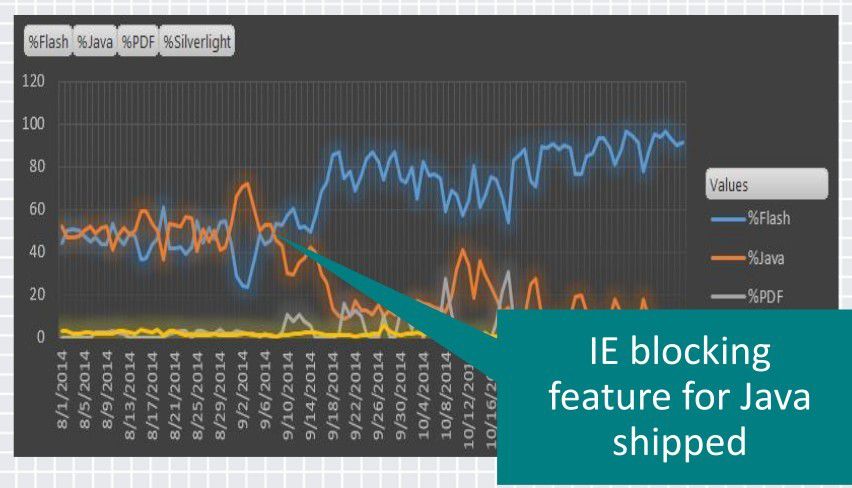
Redmond's security brains trust Tim Rains, Matt Miller, and David Watson say its patch wrecking ball applied only to out of date Java installations last year forced 90 percent of that platform's hackers to move to Flash.
“2014 saw a shift from a balanced targeting of Java and Flash to over 90 percent focus on Flash,” the team told delegates to the RSA San Francisco last week.
“The drop in Java exploits corresponds to a new Internet Explorer feature which blocks the use of out-of-date Java.”
Now the battle to build Flashy hacks is heating up. Five of eight new exploits worked into exploit kits last year targeted Adobe, while three of those five were exploited within 10 days of public vulnerability disclosure.
To illustrate the success the team say the recent HanJuan advertising Flash hole (CVE-2015-0311) bagged more than five million victims.
Microsoft however will not say whether it plans to block un-patched Flash installations, telling El Reg it does not comment on future functionality.
Almost all Windows 8.1 users run updated Flash installations; the pain is most acute for Windows 7 users of which about 20 percent have failed to patch.
Rains told Vulture South this is likely thanks to recent defensive features deployed late last year, a 70 percent drop in remote code execution (RCE) bugs, and improved Windows patching rates.
“There has been increased usage of Microsoft Update and Windows Update services over the years …. a decline of more than 70 percent in the total number of remote code execution vulnerabilities that were exploited in Microsoft products between 2010 and 2014 … fewer exploitable vulnerabilities, [and] new security mitigations,” Rains says.
Microsoft's brain trust bleats that its five Internet Explorer defences have seriously degraded the ability of blackhats to crack the browser with six exploits in 2014 being reduced to two after the hardening was switched on. The defences covered use-after-free, two Windows optional update, and its Java patch policy.
Number crunch
Both remote code execution holes and zero day vulnerabilities have fallen since 2010, making the latter flaws account for a larger percentage of total bugs.
Total zero day exploits fell 28 percent to 13 in 2013, while six RCE bugs were exploited inside of 30 days from the time of a patch release, down 86 percent since 2010.
Almost all RCE attacks over the last two years have used return oriented programming and abandoned stack corruption, the latter dropping from 54.2 percent of RCE in 2007 to nothing last year.
Rains says this is due to Redmond in 2006 killing off known vulnerable functions, particularly buffer overruns, by deprecating a subset of the C runtime library.
“At first, this requirement was simply articulated in the form of a list of bad APIs, but it changed over time to become a header file (Banned.h), that could be used in conjunction with a compiler to help provide an automated method of sanitizing source code. This became a requirement in the Microsoft Security Development Lifecycle, which developers at Microsoft use to develop software.
Two other factors that could also be contributing to this decline are the increasing prevalence of exploit mitigations for stack corruption issues (such as /GS and SafeSEH), and the increasing effectiveness of static analysis tools designed to detect such vulnerabilities."
The team's slide deck can be downloaded online [PDF].
Darren Pauli travelled to San Francisco as a guest of RSA.
Sponsored: Benefits from the lessons learned in HPC
from ffffff http://go.theregister.com/feed/www.theregister.co.uk/2015/04/27/ninety_percent_of_java_blackhats_now_finger_flash/
via IFTTT







0 comentarios:
Publicar un comentario